Queue is an abstract data structure, somewhat similar to Stacks. Unlike stacks, a queue is open at both its ends. One end is always used to insert data (enqueue) and the other is used to remove data (dequeue). Queue follows First-In-First-Out methodology, i.e., the data item stored first will be accessed first.
Queue Representation
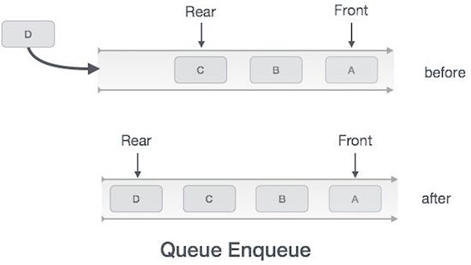
As we now understand that in queue, we access both ends for different reasons. The following diagram given below tries to explain queue representation as data structure −

As in stacks, a queue can also be implemented using Arrays, Linked-lists, Pointers and Structures. For the sake of simplicity, we shall implement queues using one-dimensional array.
Basic Operations
Queue operations may involve initializing or defining the queue, utilizing it, and then completely erasing it from the memory. Here we shall try to understand the basic operations associated with queues −
enqueue() − add (store) an item to the queue.
dequeue() − remove (access) an item from the queue.
Enqueue Operation
The following steps should be taken to enqueue (insert) data into a queue −
Step 1 − Check if the queue is full.
Step 2 − If the queue is full, produce overflow error and exit.
Step 3 − If the queue is not full, increment rear pointer to point the next empty space.
Step 4 − Add data element to the queue location, where the rear is pointing.
Step 5 − return success.
Algorithm

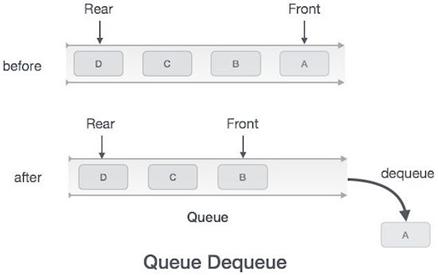
Dequeue Operation
The following steps are taken to perform dequeue operation −
Step 1 − Check if the queue is empty.
Step 2 − If the queue is empty, produce underflow error and exit.
Step 3 − If the queue is not empty, access the data where front is pointing.
Step 4 − Increment front pointer to point to the next available data element.
Step 5 − Return success.
Algorithm

